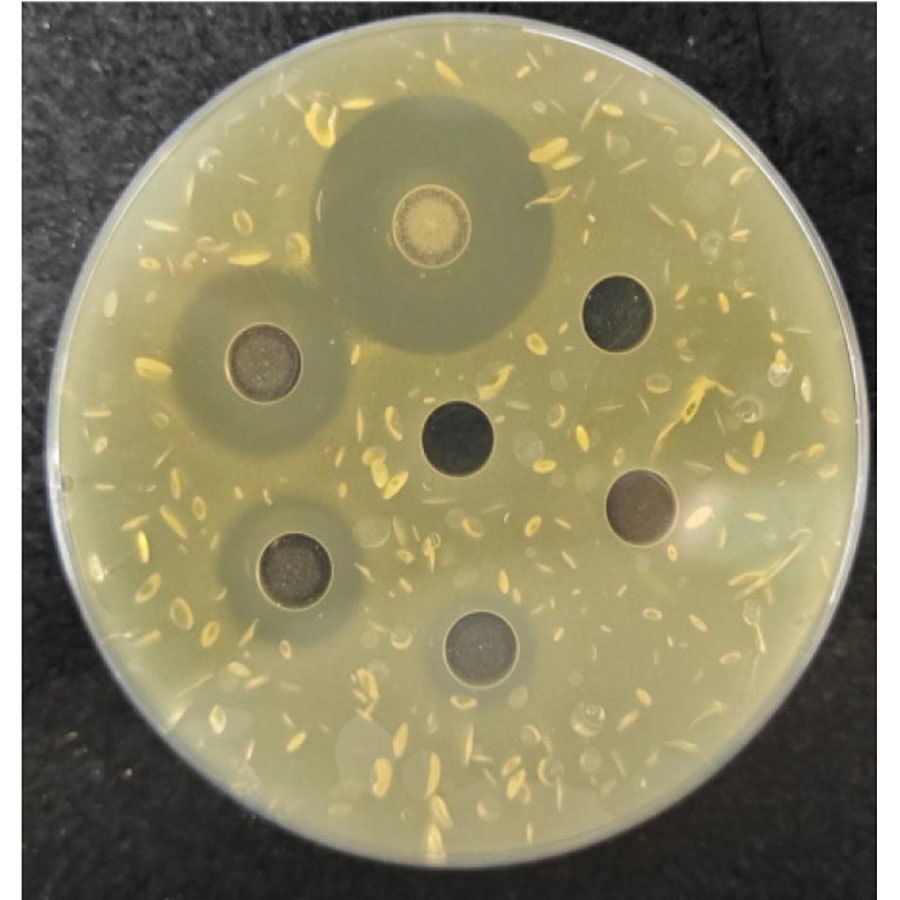
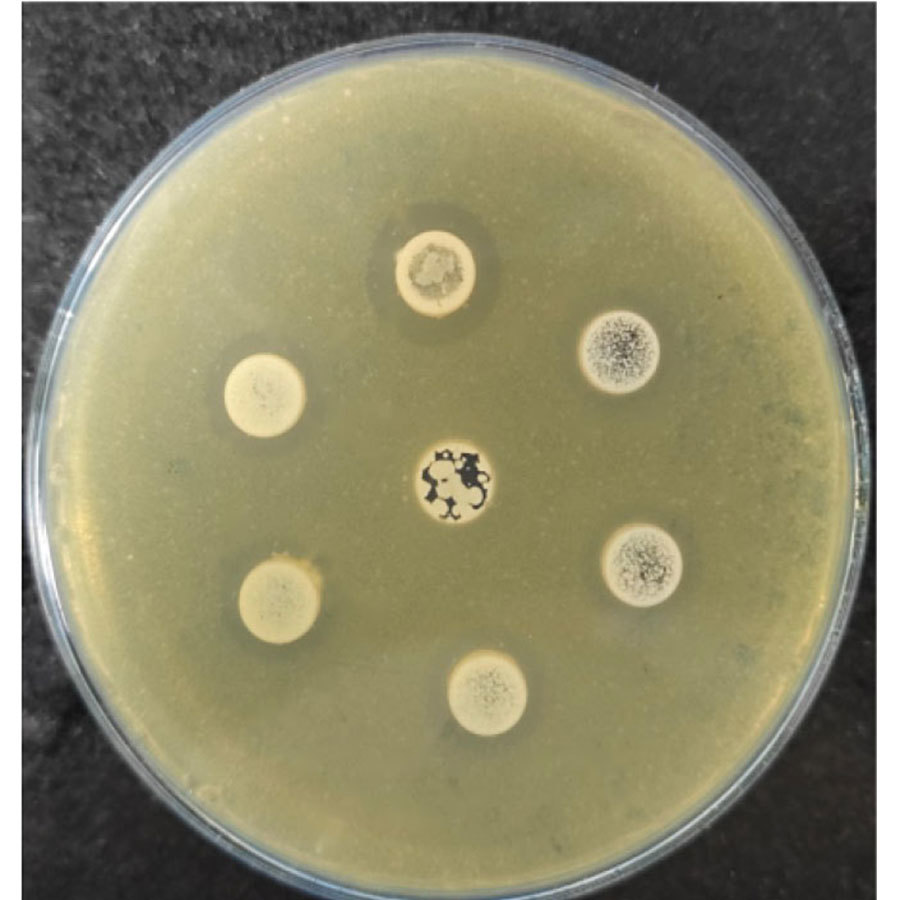
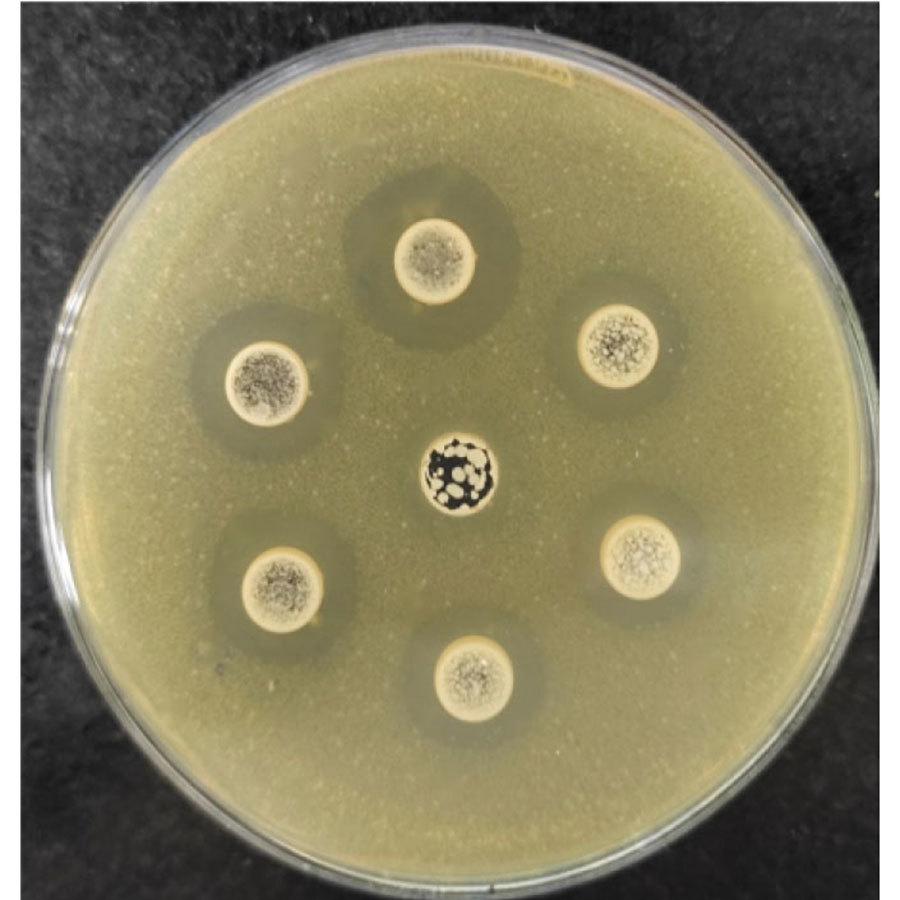
Inhibition Zone of Clostridium perfringens

Yeast Culture - Wo Feng Bao
The yeast culture Wo Feng Bao is a yeast culture suitable for ruminants, rich in nutritious active substances.
Product Introduction
The yeast culture Wo Feng Bao is suitable for ruminants and is rich in nutritious active substances. This product is made from selected specific strains, developed through a joint process by the Feed Industry Center of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and Wo Feng De, using a two-stage fermentation process of liquid pure culture and solid culture. The product is rich in functional peptides that inhibit the growth of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, organic acids, B vitamins, and yeast metabolic factors, among various active substances. It can be used in feed and farming, with benefits including increased feed intake, improved digestion rate, enhanced production performance, prevention of mastitis, and reduced incidence of calf diarrhea.
Product Efficacy
۞Increase Feed Intake
۞Improve Production Performance
۞Prevent Mastitis
۞Improve Digestion Rate and Feed Utilization
۞Promote Calf Rumen Development and Reduce Calf Diarrhea Rate
Product Composition Analysis Guarantee Value
Crude Protein ≥ 15%, Mannan ≥ 0.5%, Crude Ash ≤ 8%, Moisture ≤ 12%
Product Mechanism
The selected specific strains of the yeast culture Wo Feng Bao have strong fermentation adaptability and use a special fermentation process to obtain various active ingredients, providing sufficient nutritional substrates for the growth and reproduction of rumen microorganisms. Additionally, the fermentation process can maintain a high level of functional active ingredients, and low-temperature rapid drying can preserve a high biological activity in the final product, inhibiting the growth and reproduction of harmful microorganisms in the rumen, regulating the balance of rumen flora, effectively promoting the increase of fiber-decomposing bacteria, preventing rumen acidosis, regulating rumen health, and improving feed conversion efficiency.
Application in Dairy Cow Production
Evaluation of the Effect of Feeding Yeast Culture on Lactating Dairy Cows
The experiment selected 100 healthy lactating Holstein cows in late lactation, with similar parity (2.73±0.74), milk yield (39.94±6.98 kg/d), and lactation days (201.08±10.86). They were fed in a loose housing system, fed three times a day, with free access to water, and milked three times.
Pre-trial period of 10 days, formal trial period of 60 days.
Note: YC group, n=50 (yeast culture 125 g/d/cow) CON (control group), n=50 (yeast culture 0 g/d/cow)
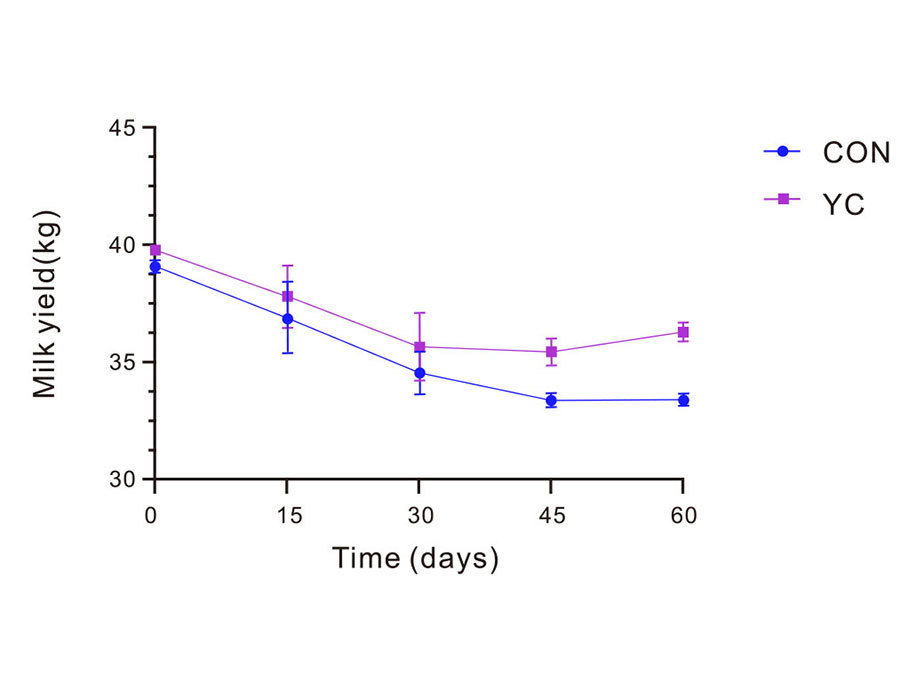
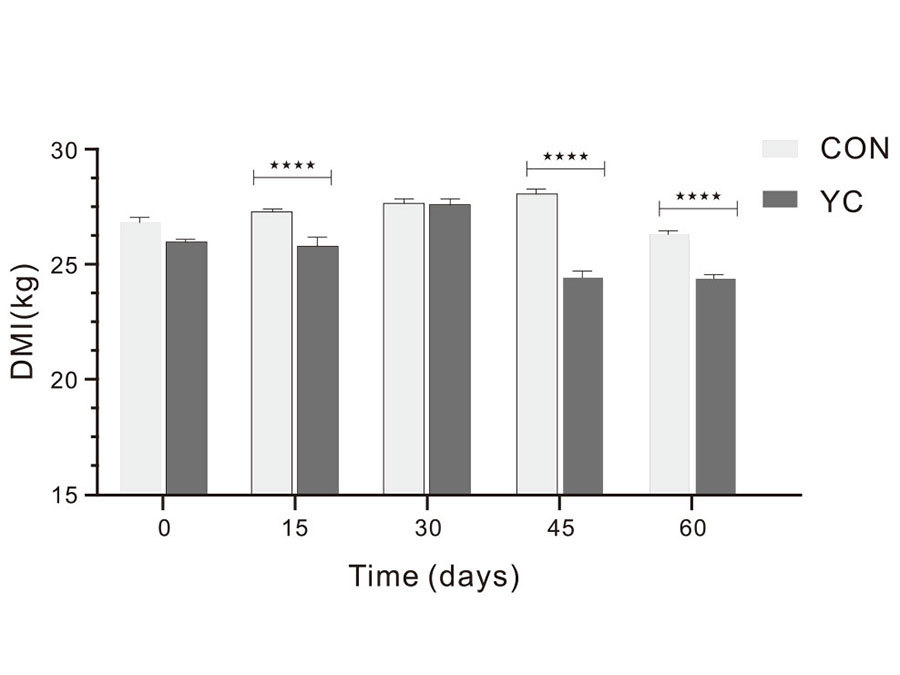
Figure: The effect of feeding yeast culture on milk yield and DMI of lactating dairy cows (n=100)
Figure: The effect of feeding yeast culture on feed efficiency of lactating dairy cows (n=100)
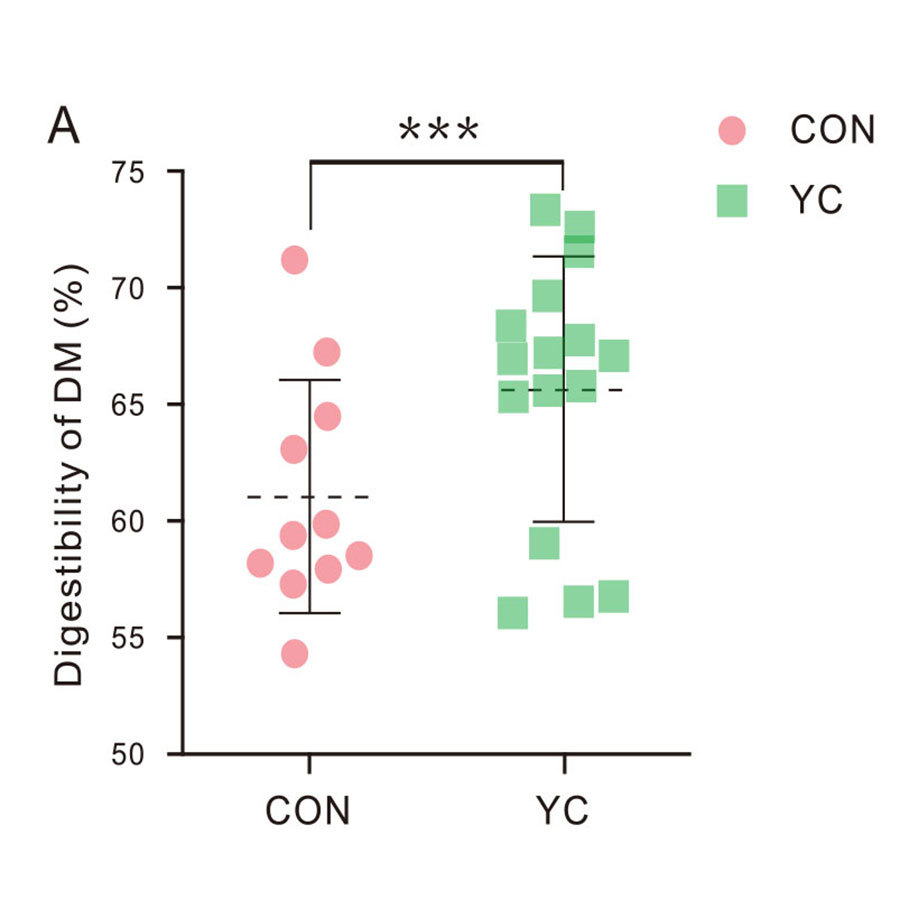
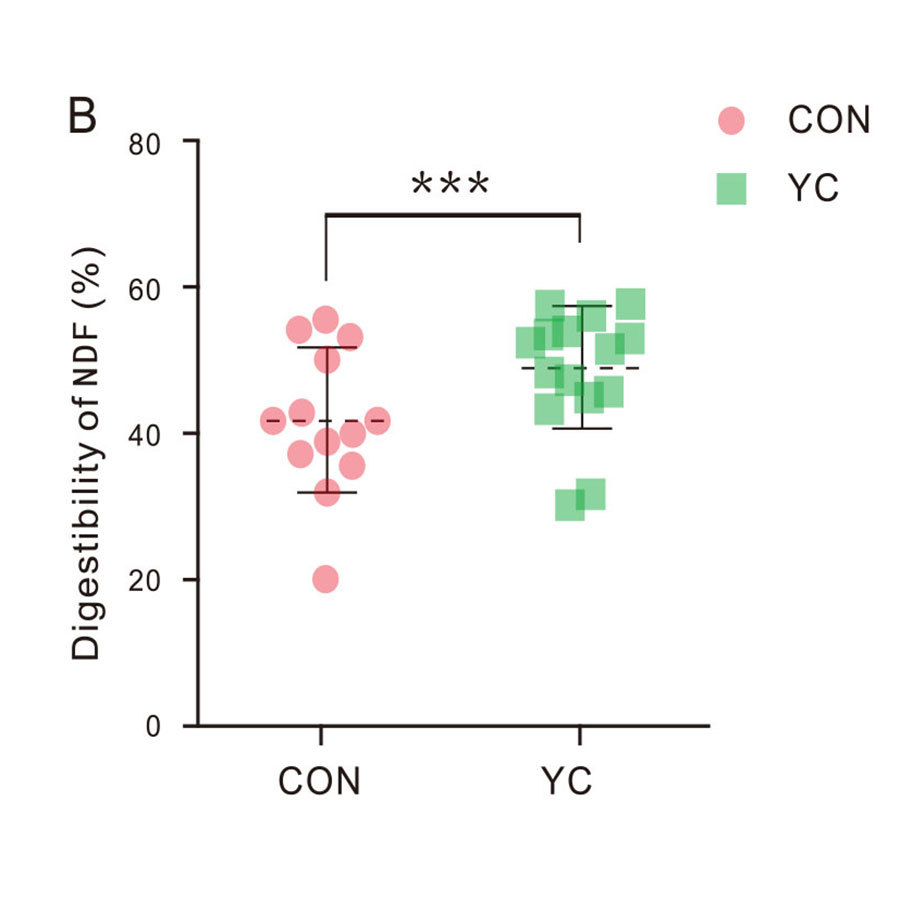
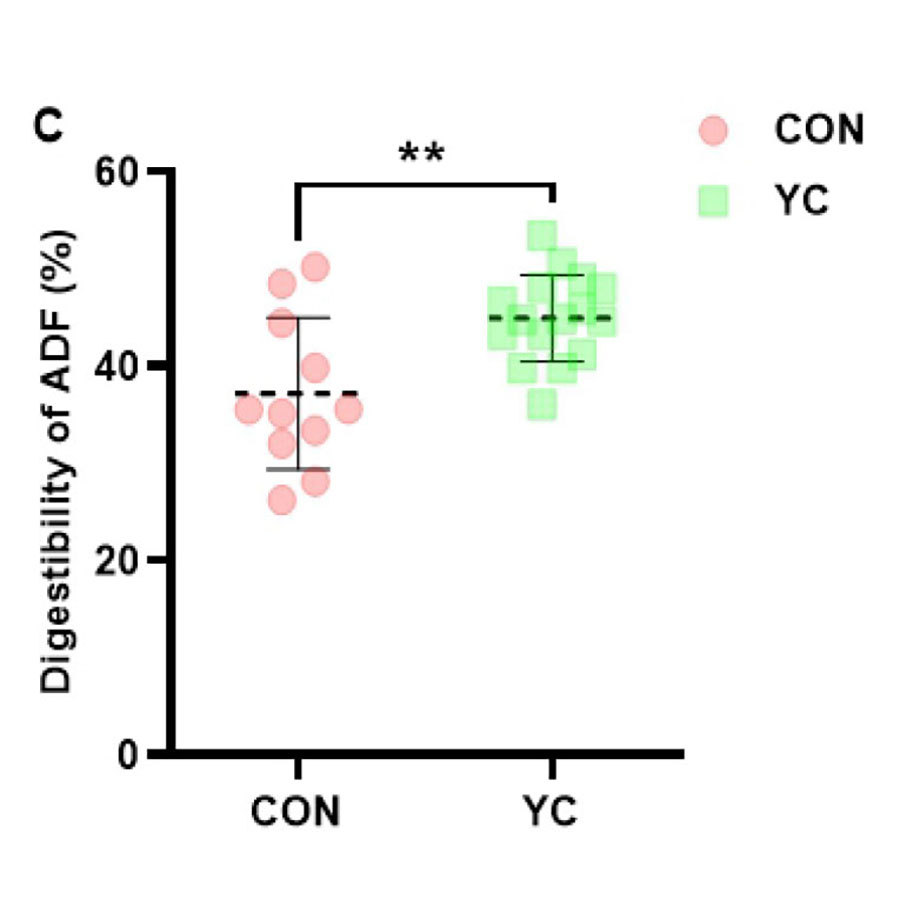
Figure: The effect of feeding yeast culture on nutrient apparent digestibility of lactating dairy cows
Table: The effect of adding yeast culture to the diet on dairy cow production performance
Item | Group | SEM | P-value | |
Items | CON | YC | ||
Milk Fat Rate /% | 5.25a | 4.76b | 0.10 | 0.02 |
Milk Protein Rate % | 3.56 | 3.43 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
Milk Lactose Rate /% | 5.08a | 5.19b | 0.02 | 0.01 |
Fat Yield, kg/d | 1.85a | 1.76b | 0.02 | 0.01 |
Protein Yield, kg/d | 1.26 | 1.27 | 0.01 | 0.55 |
Lactose Yield, kg/d | 1.80a | 1.92b | 0.02 | 0.00 |
SCC/(×104/mL) | 114.20a | 53.20b | 10.44 | 0.00 |
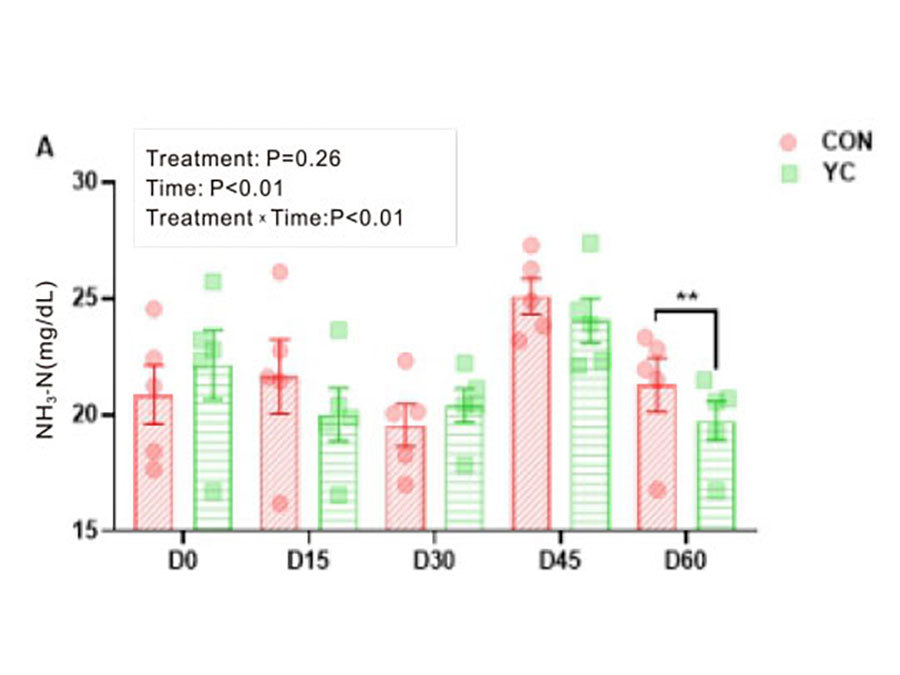
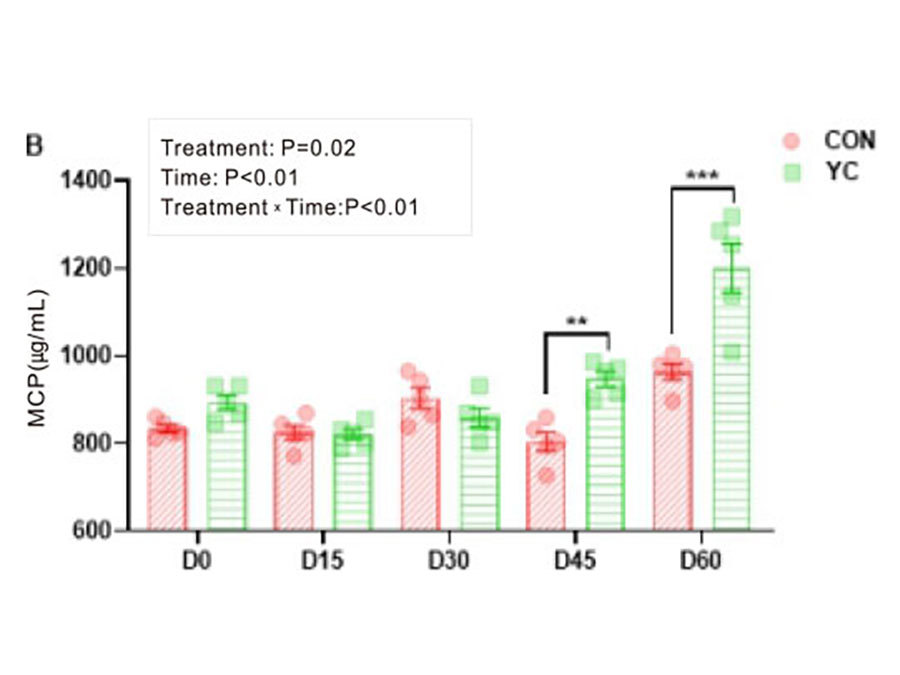
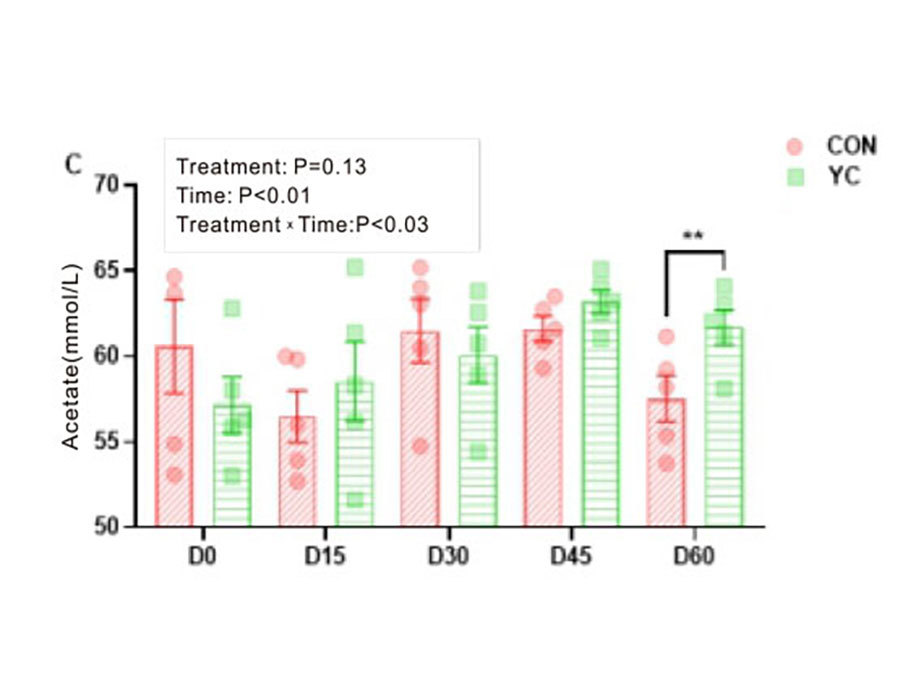
Table: The effect of adding yeast culture to the diet on dairy cow rumen fermentation
After feeding yeast culture:
۞In terms of production performance, it can increase the milk fat rate, lactose rate, and fat and lactose yield of lactating dairy cows, improving milk composition; significantly reduce the somatic cell count, thus preventing subclinical mastitis;
۞In terms of rumen fermentation in dairy cows, it can promote the synthesis of acetic acid, butyric acid, and TVFA, increasing rumen fermentation; improve propionic acid content, thereby promoting lactose synthesis and increasing milk yield;
۞In terms of nitrogen utilization, it accelerates the degradation of NH3-N, promoting the synthesis of MCP, thereby improving nitrogen utilization.
In vitro antibacterial test: has significant inhibitory effects on harmful bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella.
Dosage and Administration
Usage Instructions: Supplement 3-5 kg/t
Packaging and Storage: 20 kg/bag, kraft paper bag packaging; store in a ventilated and dry place, shelf life of 18 months.
Precautions: Use as soon as possible after opening, seal after use, and avoid moisture.
Category:
Keyword:
Related Products